Before understanding the mechanism of laser therapy for pain, let us start with how the feeling of pain is produced.Many diseases are accompanied by pain. When the body is strongly stimulated by the outside world or endogenous stimulation, when the stimulation reaches a certain intensity, it will stimulate the nerve endings, and transmit the noxious nerve impulses from the peripheral end to the spinal ganglion cells and their central ends through the pain-transmitting nerve fibers A and C fibers, and finally reach the posterior horn of the spinal cord, causing the posterior horn cells to be excited, producing “nociception”, and further transmitting to the higher center to produce pain. Pain, especially pain caused by shoulder, neck, waist, leg, joint and muscle injuries, is the most common health problem encountered by many middle-aged and elderly people. Pain not only affects normal life and work, but also brings negative damage to mental emotions! Therefore, pain management is increasingly valued by people. As the side effects of opioid analgesics become increasingly obvious, people are more willing to choose non-drug physical therapy to solve pain problems. With the rapid progress of high-tech laser technology in the field of medicine, a new generation of high power laser physiotherapy has been born, especially in pain management, and has been widely used around us. Laser therapy for pain can penetrate up to 12cm into the tissue, can produce photobiomodulation effects on deeply damaged tissues, and can quickly improve acute and chronic pain. After about 10 minutes of treatment, the pain can be significantly relieved.
Mechanisms of laser therapy for pain
A large number of scientists have used lasers to conduct experiments on the treatment of pain diseases. From the experimental results, lasers have the effect of relieving pain and reducing or eliminating the vicious cycle of such painful diseases. The Mechanisms are as follows:
① Laser therapy for pain can directly stimulate the release of endogenous endorphins and enkephalins through the use of biological stimulation and mechanical stimulation, thereby inhibiting the conduction of Aδ and C fibers. According to the pain gate control mechanism, mechanical stimulation of free nerve endings leads to the inhibition of pain conduction, thereby relieving pain
② Irradiation with high intensity laser therapy can regulate the content of serotonin (also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine/5-HT). Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. Serotonin binds to receptors (5-HT3) and sensitizes nociceptors. Antagonists acting on peripheral serotonin receptors (5-HT2A and 5-HT3) can reduce the pain generated by tissues.
③ Irradiation with lasers for pain can reduce bradykinin. Bradykinin is an important cytokine that can mediate inflammatory effects. It acts on pain receptors to cause pain and plays an important role in mediating inflammatory pain. Bradykinin has a wide range of effects. It can sensitize sensory neurons, especially in the process of pain generation. Inflammatory pain, rheumatoid pain, and pain caused by hypoxia are all accompanied by an increase in bradykinin concentration. Therefore, the reduction of bradykinin can effectively relieve tissue pain.
④ Irradiation with laser can regulate the function of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is an excitatory transmitter. Due to the existence of two different acetylcholine receptors, it has two different effects, excitatory and inhibitory. Acetylcholine receptors (AChR) are divided into two subtypes, namely muscarinic cholinergic receptors (mAChR) and nicotinic cholinergic receptors (nAChR). The manifestations of ACh acting on mAChR are: cardiac inhibition, vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, increased glandular secretion (such as salivation), and miosis (myopia); the manifestations of ACh acting on nAChR are: skeletal muscle contraction and ganglion excitation. By irradiating laser, the function of acetylcholine receptors is regulated, which can inhibit nerve excitement, vasodilation, increase blood circulation, and relieve pain.
⑤At the same time, laser treatment for pain irradiation also has an anti-inflammatory effect, which can activate or induce T, B lymphocytes and macrophages to produce cytokines, activate the systemic immune system through lymphocyte recirculation, enhance phagocytic ability, improve nonspecific immunity and specific immunity, reduce the pain caused by the activation of nerve fibers during inflammatory reactions, and effectively reduce swelling caused by inflammation.
⑥Laser therapy irradiation of the sympathetic ganglia in the affected area can cause increased blood flow, improve local blood circulation, increase cell metabolism, promote peripheral circulation and lymphatic detoxification in the lesion area, and combine biostimulation effects and photochemical effects to provide non-addictive pain management while promoting tissue healing.
⑦Laser therapy for pain can also reduce the pain caused by wound stimulation. Laser irradiation can promote more oxygen atoms to reach the mitochondria, and at the same time promote the terminal enzyme cytochrome C oxidase of the cell respiratory chain to accelerate the production of ATP, thereby promoting the regeneration and healing of damaged tissues and achieving the therapeutic purpose of relieving pain.
What types of pain are mainly treated with laser therapy?
① Joint and soft tissue pain
A study used conservative treatment (interferential current and ultrasound) to treat patients with knee osteoarthritis, followed by laser therapy. The results showed that the visual analog score and the Korean Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index were significantly improved.
② Neck and back pain
A study compared the efficacy of traction therapy and laser therapy in the treatment of cervical spondylosis. The results showed that both treatments improved the efficacy and analgesia of patients immediately after treatment and 4 weeks after treatment, while the laser therapy group was more effective than the traction therapy in the long-term follow-up (after 12 weeks).
③ Neuropathic pain
Alayat et al. published a clinical study on HILT for the treatment of facial nerve paralysis. The results showed that laser irradiation has a good repair effect on nerve damage.
Clinical operation of laser treatment for pain
During laser treatment for pain in order to achieve better treatment effects in clinical practice, doctors need to be proficient in the following operating techniques and understand the relevant precautions:
① Laser irradiation method
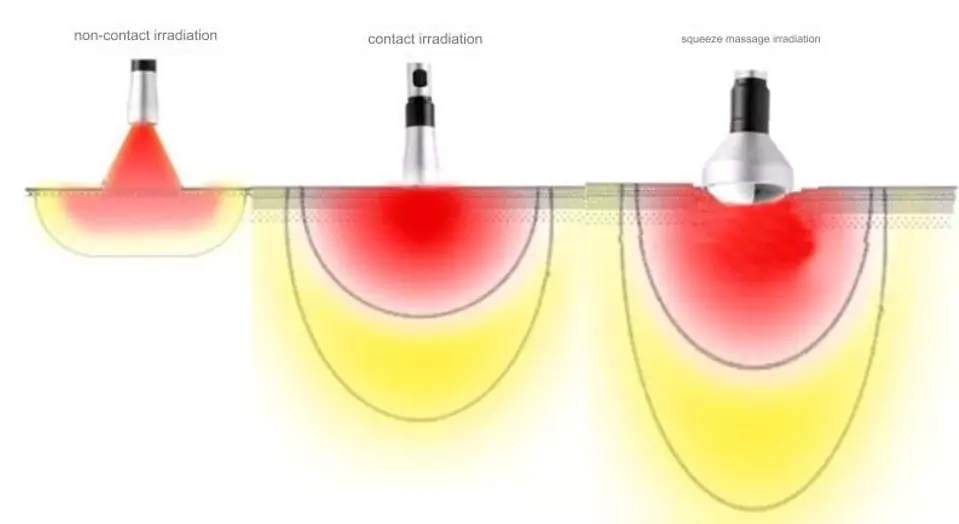
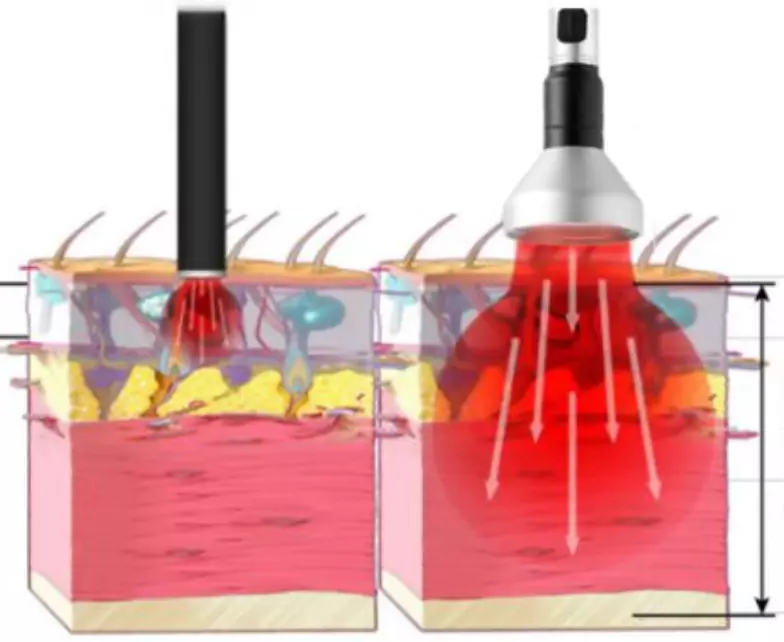
In clinical treatment, different laser irradiation methods need to be selected according to different symptoms to achieve better treatment effects. When suffering from diseases such as muscle pain or joint pain, tender point irradiation can be used to squeeze and massage the treatment area; for animals with neurological diseases, irradiation can be performed along the nerve direction, or more nerve cells can be irradiated around the treatment area in a “Z” shape or circular circle; sometimes direct contact of the probe with the skin will also increase pain, so non-contact irradiation is used.
② Irradiation time
In pain clinics, the length of irradiation time is not only related to time and efficiency, but also to the effectiveness of the treatment. Laser irradiation has a stimulating effect on nerve endings, and long-term stimulation will cause nerve fatigue. If irradiation continues at this time, the activation of tissues and cells will be reduced, and it is impossible to achieve the expected treatment effect.
③ Temperature control
Temperature control is also very important during laser treatment for pain. During use, it is also necessary to properly adjust the laser power, irradiation time, and spot size during treatment according to the animal’s hair and skin color. These factors can affect the temperature when the laser irradiates the skin. Too high a temperature can cause burns on the surface of the animal, cell death in the body, and unnecessary pain.
④Choice of wavelength
For pain diseases in different parts of the body, lasers of different wavelengths need to be selected to ensure that the desired treatment area can be reached during irradiation to achieve the expected therapeutic effect. The effect of high power laser therapy is determined by power and wavelength. The optimal laser wavelength in the tissue should be 650-1100nm.
The advantages of laser therapy for pain
Compared with other treatment methods, the advantages of laser treatment for pain include:
① No pain
Laser treatment is a non-invasive treatment, which is more friendly to patients who are prone to stress reactions and can improve the safety factor and job satisfaction of doctors;
② No side effects
Laser therapy for pain is a drug-free and surgery-free treatment, and there are very few reports of adverse reactions to laser treatment;
③ Wide range of applications
Whether it is chronic pain or acute pain, good treatment effects can be achieved through correct operation methods and appropriate treatment cycles. In the treatment of other systemic diseases, laser can play a therapeutic role;
④ Good treatment effect
The biostimulation mode of high power laser has a photothermal treatment effect, which can better relax muscles, relax trigger points, promote fluid circulation and tissue repair, and further improve the treatment effect;
⑤ Fast effect
Higher treatment power can generate more treatment photon energy, greatly reducing the treatment time of laser therapy and improving clinical treatment efficiency. Generally, cases can show significant improvement after 3-4 irradiations, and can recover after 1 course of irradiation;
⑥ Simple operation
For busy doctors, laser treatment for pain is more convenient to operate, and the single treatment time is short, which helps hospitals improve diagnosis and treatment efficiency.
In summary, laser therapy for pain has been widely used in the clinical treatment of human and animal pain diseases due to its significant advantages. Laser therapy has great development prospects in the field of rehabilitation physical therapy. However, there is still a lot of room for improvement in clinical research reports surrounding laser treatment for pain. It is hoped that in the future, more high-quality basic research can be conducted to provide doctors with real and reliable conclusions when using laser therapy to treat pain, and to further clarify the specific mechanism and operating specifications of laser therapy, forming a more unified standard of use, and providing a basis for treatment. More specialized help is available for pain.
